Xslt Xsl Template Match
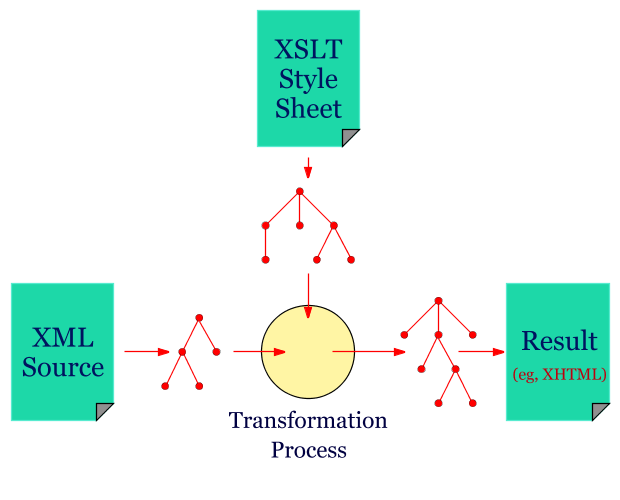
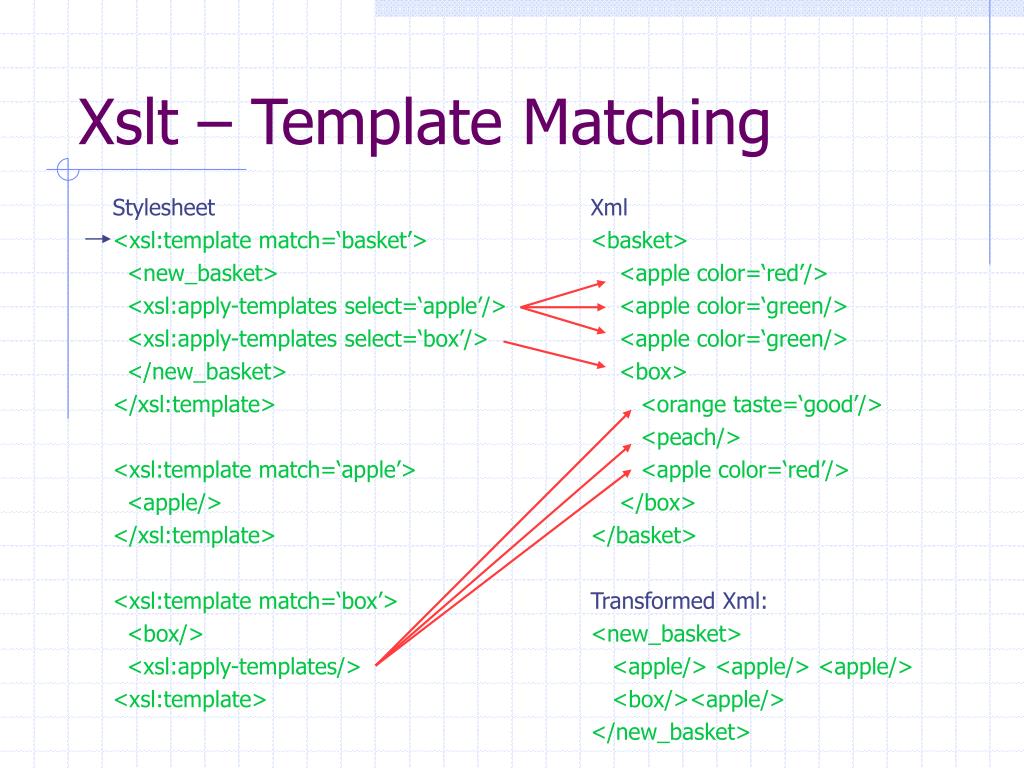
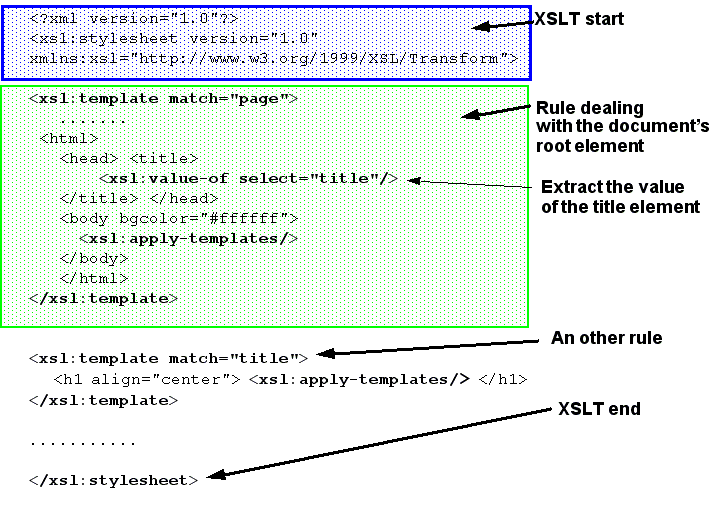
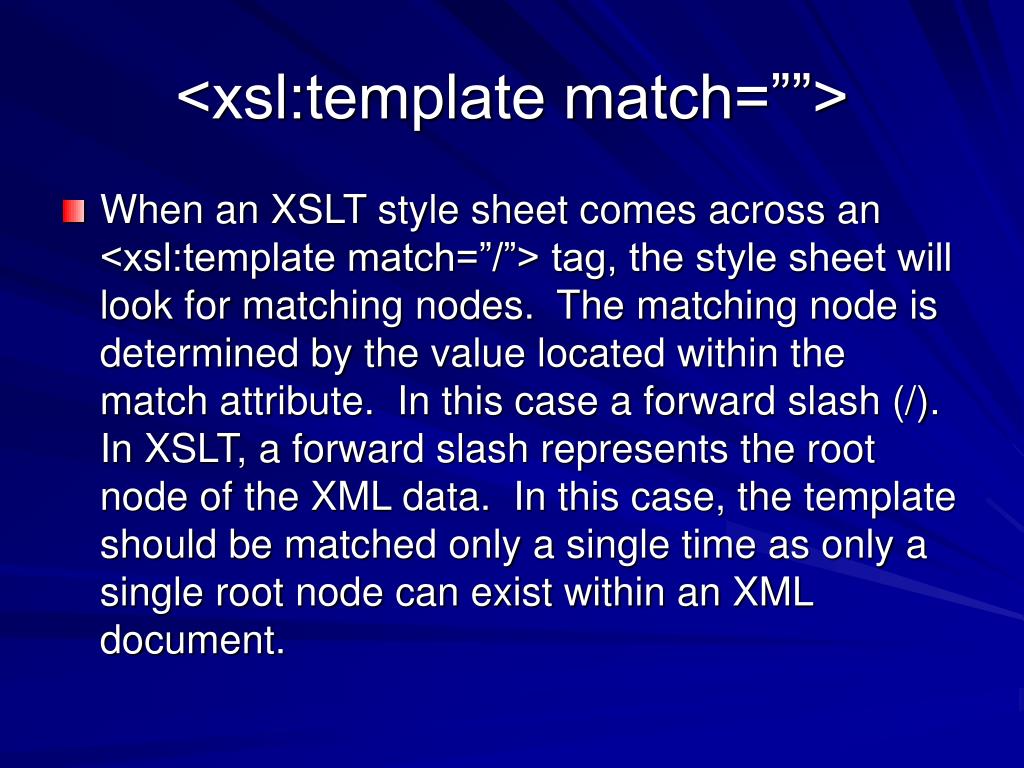
Xslt Xsl Template Match - The match attribute can also. If we add a select attribute to the element, it.</p> A template is invoked by the processor when called by name or when it matches a xml node. /> in your solution, you are transforming all. I am working with xslt 2.0 and trying to apply the same transformation process to both elements from the input xml and elements dynamically created within the xslt. The element applies a template to the current element or to the current element's child nodes. The xsl:template element with match=/root matches the root element of the xml document and copies it to the output. There are a few problems with this match pattern: Specifies a name for this template, by which it can be invoked through the element. /|@*|node() is a match pattern composed of three single patterns. / matches a root node, also called document node, @* matches any attribute node and node() as a pattern. The element is used to build templates. The match attribute on the element contains a pattern expression. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. Specifies a name for this template, by which it can be invoked through the element. There are a few problems with this match pattern: Therefore, the names of the elements to be. The match attribute is used to associate the template with an xml element. I am working with xslt 2.0 and trying to apply the same transformation process to both elements from the input xml and elements dynamically created within the xslt. The match attribute indicates on which parts the template transformation is going to be applied. The value you have to provide. The element is used to build templates. The xsl:template element with match=/root matches the root element of the xml document and copies it to the output. The match attribute is used to associate a template with an xml element. The match attribute on the element contains a pattern expression. The match attribute can also be used to define a template for. The xsl:template element with match=/root matches the root element of the xml document and copies it to the output. The element is used to build templates. To build templates, the element is used and to associate a template with an xml element, the match attribute is used. The. / matches a root node, also called document node, @* matches any attribute node and node() as a pattern. I am working with xslt 2.0 and trying to apply the same transformation process to both elements from the input xml and elements dynamically created within the xslt. There are a few problems with this match pattern: To build templates, the. The match attribute is used to associate a template with an xml element. A template in xslt is the equivalent of a method in java. The xsl:template element with match=/root matches the root element of the xml document and copies it to the output. The element applies a template to the current element or to the current element's child nodes.. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. To build templates, the element is used and to associate a template with an xml element, the match attribute is used. The match attribute can also. Specifies a name for this template, by which it can be invoked through the element. Again, to define a template for. There are a few problems with this match pattern: Therefore, the names of the elements to be. The match attribute can also. If we add a select attribute to the element, it.</p> To build templates, the element is used and to associate a template with an xml element, the match attribute is used. I am working with xslt 2.0 and trying to apply the same transformation process to both elements from the input xml and elements dynamically created within the xslt. The element contains rules to apply when a specified node is matched. The element applies a template to the current element or to the current element's child nodes. Again, to define a. Again, to define a template for the entire xml document,. The xsl:template element with match=/root matches the root element of the xml document and copies it to the output. / matches a root node, also called document node, @* matches any attribute node and node() as a pattern. The match attribute indicates on which parts the template transformation is going. The match attribute can also. There are a few problems with this match pattern: This then allows you to define a template for each element you are interested in and process the xml in a more. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. To build templates, the element is used and to associate a. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched. The element is used to build templates. This then allows you to define a template for each element you are interested in and process the xml in a more. /> in your solution, you are transforming all. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml. This then allows you to define a template for each element you are interested in and process the xml in a more. The match attribute indicates on which parts the template transformation is going to be applied. The match attribute can also be used to define a template for. I am working with xslt 2.0 and trying to apply the same transformation process to both elements from the input xml and elements dynamically created within the xslt. A template is invoked by the processor when called by name or when it matches a xml node. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. /|@*|node() is a match pattern composed of three single patterns. There are a few problems with this match pattern: / matches a root node, also called document node, @* matches any attribute node and node() as a pattern. The element contains rules to apply when a specified node is matched. The xsl:template element with match=/root matches the root element of the xml document and copies it to the output. If we add a select attribute to the element, it.</p> Specifies a name for this template, by which it can be invoked through the element. The syntax is the same as that used to select nodes with , , and.</p> The element applies a template to the current element or to the current element's child nodes.Overview of XSLT and XPath
Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match Xslt Design Patterns Ppt Download williamsonga.us
Xsl Template Match
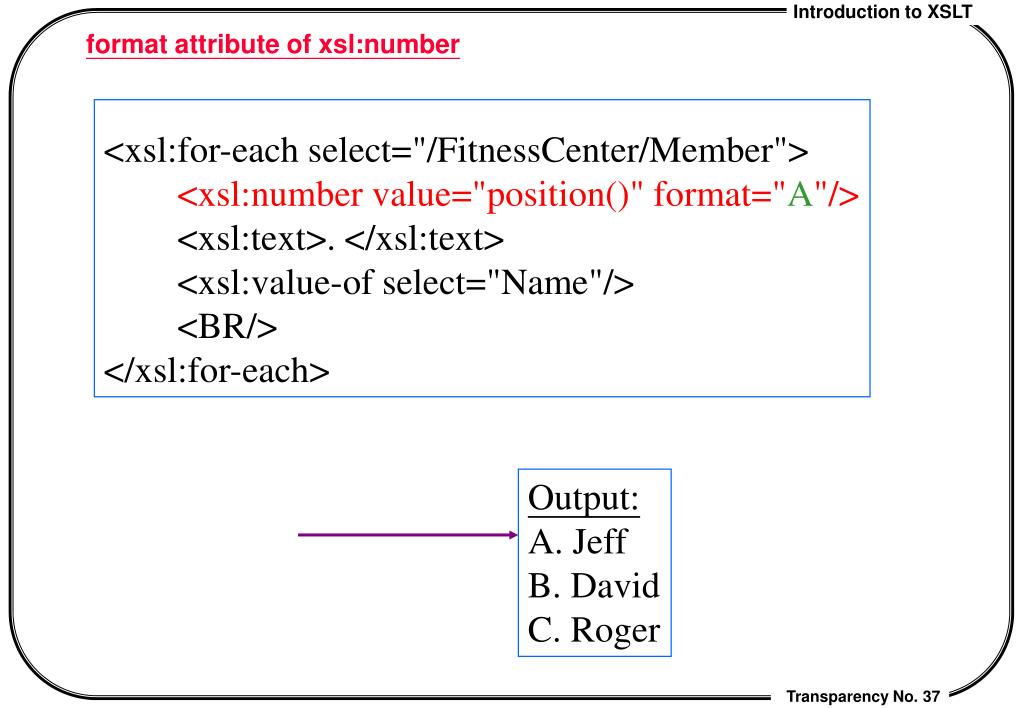
PPT Introduction to XSLT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Xsl Template Match
Xsl Apply Templates
Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match
The Match Attribute Can Also.
The Value You Have To Provide.
A Template Matches Nodes, Not Strings.
To Build Templates, The Element Is Used And To Associate A Template With An Xml Element, The Match Attribute Is Used.
Related Post: